What is Phenix
Phenix is a comprehensive software package for macromolecular structure determination for crystallographic (X-ray, neutron, and electron) and electron cryo-microscopy data.
A hightly automated software system
Phenix is a highly automated software system for macromolecular structure determination. It can rapidly provide an initial partial model of a structure without significant human intervention, given moderate resolution and good quality data. This is thanks to the development of new algorithms for maximum-likelihood molecular replacement (Phaser), heavy-atom search (HySS), template and pattern-based automated model-building (Resolve), and automated macromolecular refinement (phenix.refine). These algorithms are based on a comprehensive set of crystallographic libraries available to the community (cctbx). The algorithms are easily accessible to users through the Phenix GUI and the command line.
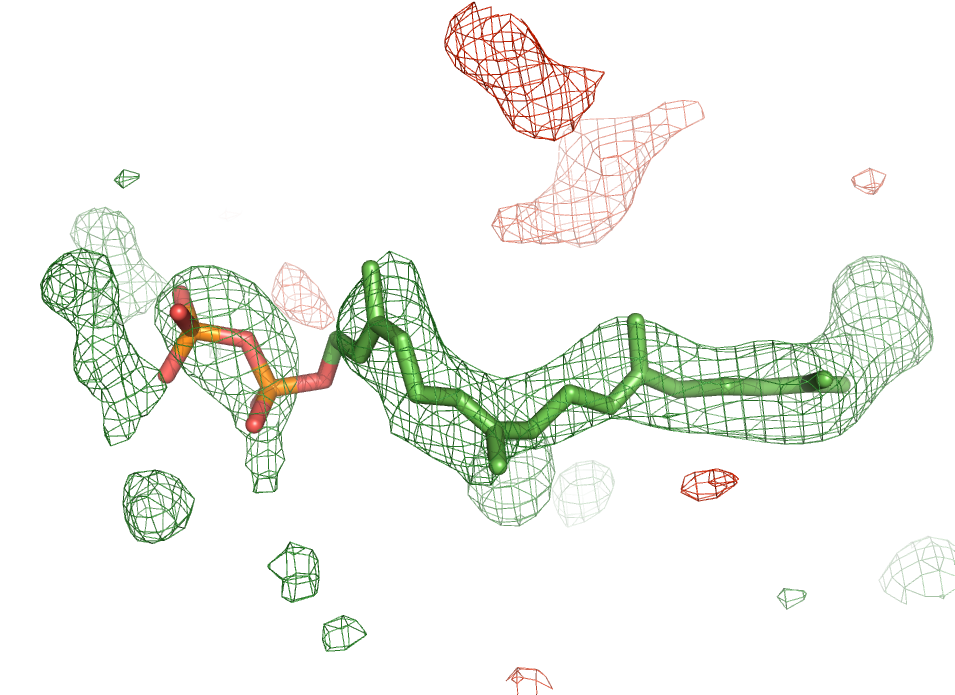
Convenient ligand handling tools
Phenix also includes a number of tools for handling ligands. Automated fitting of ligands into the electron density is facilitated via the LigandFit wizard. Besides being able to fit a known ligand into a difference map, the LigandFit wizard can identify ligands on the basis of the difference density only. For ligands whose chemical description is not available in the supplied monomer library, the electronic ligand builder and optimization workbench (eLBOW) can be used to generate stereo chemical dictionaries for the use in restrained macromolecular refinement.
An environment for scientific computing
Phenix builds upon Python, the Boost.Python Library, and C++ to provide an environment for automation and scientific computing. Many of the fundamental crystallographic building blocks, such as data objects and tools for their manipulation, are provided by the Computational Crystallography Toolbox (cctbx). The computational tasks that perform complex crystallographic calculations are then built on top of this. Finally, there are a GUI and command line user interfaces available in Phenix. In order to facilitate automated operation, Phenix uses Project Data Storage (PDS) to store and track the results of calculations.

A diverse and multi-national team
The Phenix development team consists of members from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Paul Adams's group), New Mexico Consortium and Los Alamos National Laboratory (Tom Terwilliger's group), Cambridge University (Randy Read's group), and Duke University (David and Jane Richardson's group). Researchers from Texas A&M University (Tom Ioerger's and Jim Sacchettini's groups) participated in the first five years of Phenix development.
Funding
Phenix is funded by the National Institutes of Health (General Medicine) under grant P01GM063210, and the Phenix Industrial Consortium.
Citing Phenix
If you use Phenix to solve a structure, please cite this publication:
Macromolecular structure determination using x-rays, neutrons and electrons: recent developments in phenix. D. Liebschner, P. V. Afonine, M. L. Baker, G. Bunkóczi, V. B. Chen, T. I. Croll, B. Hintze, L. W. Hung, S. Jain, A. J. McCoy, N. W. Moriarty, R. D. Oeffner, B. K. Poon, M. G. Prisant, R. J. Read, J. S. Richardson, D. C. Richardson, M. D. Sammito, O. V. Sobolev, D. H. Stockwell, T. C. Terwilliger, A. G. Urzhumtsev, L. L. Videau, C. J. Williams, P. D. Adams. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 75, 861–877 (2019). doi:10.1107/S2059798319011471.Publications
A number of publications describing Phenix can be found here.
